AI avatars on one hand, humanoid robots on the other: multimodal technology is blurring the boundary between virtual and real
![]() 04/09 2025
04/09 2025
![]() 513
513
Text/VRGyro
Not long ago, Alibaba deployed a real-time high-quality rendered 3D AI avatar TaoAvatar on Apple's Vision Pro using 3D Gaussian Splatter technology, which can generate lifelike, topologically consistent 3D full-body virtual avatars from multi-view sequences, with full control over poses, gestures, and expressions.

This technology enables avatars to listen, speak, express emotions, and move in 3D space. The same avatar can instantly switch professions/clothing and can be applied to AR e-commerce live streaming scenarios in the future. It can be applied to virtual shopping guides and other fields in the future.
On April 7, Ali Tongyi announced the open-source release of the LHM drivable ultra-realistic 3D avatar generation model, which can generate ultra-realistic 3D avatars in seconds from a single image. By inputting just one image, one can engage in low-latency real-time conversations with the avatar generated from that image. In the future, LHM has three application directions: motion reproduction, game character generation, and virtual reality exploration.
The development of avatars is much faster than imagined, and AI is just a microcosm of its transformation.
Virtual anchors, digital employees... When avatars start to access AI
Kizuna AI, a virtual VTuber that has been dormant since 2022, recently "resurrected" with a new image, resumed updates on YouTube, and announced that it will focus more on music activities in the future. Shortly after the update, its YouTube subscriptions surpassed 3 million again.

The left image shows Kizuna AI's new image
Netizens joked: "In 2016, I wondered if Kizuna AI was AI; in 2025, I'm still wondering if Kizuna AI is AI. Everything has come back!"
Kizuna AI, which positions itself as artificial intelligence, may not have anticipated that, also in 2022, after announcing an indefinite hiatus, the true AI chatbot ChatGPT would spark a global wave, pushing AI development to new heights.
Continuous technological upgrades continue to expand the "working abilities" of avatars. Compared to avatars (virtual anchors, virtual idols, etc.) driven by humans (the person inside), AI-driven avatars (AI assistants, AI digital employees) are now favored more after accessing multimodal large models.
In the field of virtual anchors, AI VTubers have sprung up like mushrooms after rain. For example, Neuro-sama is a fully AI-operated English-speaking VTuber that can not only respond to chats but also play games like
The difference between them and traditional virtual anchors is that the latter do not require much human intervention, can interact with viewers autonomously based on large language models (LLMs), and can respond to user chats, play video games, and share personal anecdotes in real-time. As developers provide them with updated data or language models, they can continuously evolve.
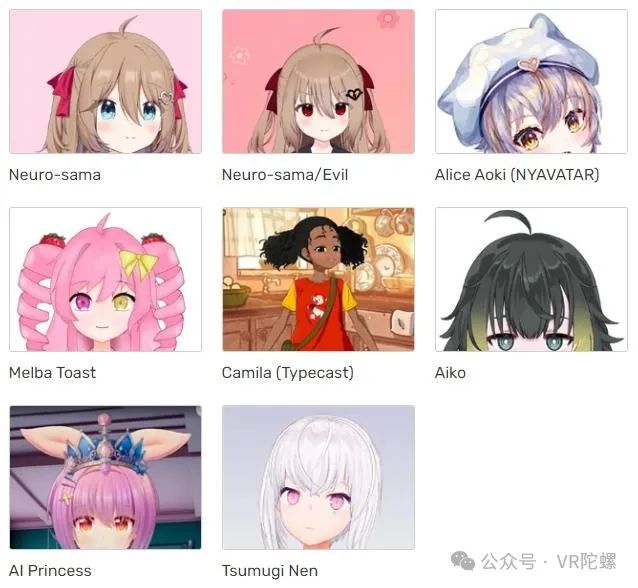
AI-driven VTuber
With the continuous maturation of multimodal large models, the functional attributes of avatars in different positions are changing: AI avatars are reshaping the boundaries of human-machine interaction:
During the Spring Festival, the AI anchor "Xiaoyu" of Hangzhou TV News simulcast conducted news broadcasts with a 0% error rate. Many local TV stations and local media fusion centers have hired AI avatars as anchors.
During the 2025 Two Sessions, the Changjiang Daily officially launched the latest AI product integrated with DeepSeek, and the avatar "Xiaowu" can conduct knowledge Q&A based on the content of the government work report.

A business owner in Yiwu, Zhejiang, uses AI avatar short video production tools to record videos with lip-syncing and pair them with corresponding product copy to generate corresponding foreign language videos with one click.
Tencent Cloud Intelligence's digital intelligence connects to the DeepSeek large model. Users can use models such as V3 and R1 built into the digital intelligence platform to give DeepSeek a real human appearance without development. Digital intelligence can be applied to interactive and broadcasting scenarios.
Baidu Huibo Xing released the "One-Click Clone of Real Person" avatar live streaming function, which enables synchronized replication of voice, image, and decoration without professional equipment, manned supervision, or an operation team, and allows users to create a digital human e-commerce live streaming room with one click by uploading a video.
Unknowingly, AI large models such as DeepSeek are infusing new blood into avatars. Avatars are evolving from "skin" to "soul," and AI will gradually cover the entire process from avatar production to application.
Evolution of abilities, this is what AI avatars should look like
The development of avatars can be divided into five stages based on technological maturity: the budding stage, the initial stage, the growth stage, and the mature stage, each with its distinctive characteristics.
Avatars in the budding stage originated from Japanese otaku culture in the 1980s, emerging as character concepts. Until the initial stage of the early 21st century, with the launch of Yamaha's VOCALOID voice synthesis software, avatars officially stepped onto the cultural and entertainment stage, with Hatsune Miku as the representative character. From 2016 to 2020, the development of motion capture technology and recording equipment reached a new stage, giving rise to virtual anchors like Kizuna AI that required the person inside to drive them.

Avatars entering the growth stage are mainly pixiv style images. After the rise of the metaverse in 2021, AI began to be integrated into the production of avatars. Upgrades in modeling, driving, and rendering technologies have enabled 3D ultra-realistic avatars to gain high attention due to their highly realistic appearance and interactive capabilities, with representative characters such as AYAYI and Liu Yexi. However, these avatars come with IP attributes, and their high production costs make it difficult to replicate their model and launch them into the market in large quantities.
Before officially entering the mature stage, the avatar industry took a new branch due to the emergence of AI such as ChatGPT. During this period, the integration of various industries with avatars became closer, and AI was no longer limited to being integrated into the production process of avatars but could directly endow avatars with the ability to express emotions, output content, and apply on a large scale.
Purely AI-driven avatars have reached new heights, and their technical composition mainly covers aspects such as external appearance, decision-making interaction, and multi-end deployment.
External appearance: Significant progress has been made in the shaping technology of AI avatars' external appearance, thanks to breakthroughs in computer graphics, computer vision, neural networks, and deep learning. Traditional modeling methods are cumbersome and have limited effects. Nowadays, avatar modeling algorithms can generate new samples from a small number of perspective images/videos/audios, and then render the data to generate more realistic 3D avatar images.
EchoMimicV2 avatar – Input 1 image + 1 gesture video + 1 audio to generate an avatar with natural movements
Decision-making interaction: Realizing smooth and intelligent interaction between AI avatars and users relies on capabilities such as speech recognition (ASR), speech synthesis (TTS), natural language understanding (NLP), AIGC, large language models (LLMs), as well as the construction of knowledge graphs and deep learning capabilities to complete analytical decisions and realize real-time interaction with avatars. In ToB application scenarios such as smart customer service and smart screens, AI avatars perform exceptionally well.
Tavus: Real-time audio and video conversation avatar – Can hear, see, understand users' words, and respond with emotion
Multi-end deployment: Multi-end deployment is crucial for the value of AI avatars. Practical AI avatars need to support multi-platform operation, which means they require strong transmission capabilities, cloud computing, edge computing, and other capabilities to ensure high-quality and low-latency human-machine interaction services.
Silicon-based intelligence open-source real-time avatar duix.ai – Can be deployed on various terminal devices
The above avatars are realistic enough in terms of appearance and facial expressions, and what users desire is a more "living" avatar. On February 6, ByteDance launched the OmniHuman-1 avatar model, which can generate realistic full-body dynamic videos from a single photo and a piece of audio. It is reported that OmniHuman was trained with over 18,700 hours of human video data.

ByteDance's OmniHuman-1 avatar model
On the track of AI avatars, we can see the participation of companies such as Alibaba, Baidu, JD.com, and Tencent. Now, AI avatar products and landing scenarios have been verified, but the most critical cost issue will further ease with the increase in domestically trained models.

Silicon-based avatar HeyGem.ai model
On March 6, Silicon-based Intelligence open-sourced the silicon-based avatar HeyGem.ai model on GitHub. Users only need to upload a 1-second video or a real person's photo to output a 60-second avatar video that restores the person's voice and appearance within 30 seconds, and it supports offline cloning of the avatar's image and voice, as well as 4K resolution export. With the release of this open-source model, developers, enterprises, and even individual users can create AI avatars at a lower cost.
When AI avatars build a complete interactive ecosystem in the virtual world, the boundaries of technology are quietly extending to the physical world.
Another evolution direction of AI: Embodied intelligence - humanoid robots
As one of the first applications of AI large models to attempt commercialization, AI avatars are seen by many as a gateway for human-machine interaction and can now communicate with humans without barriers. With technological advancements, people can't help but wonder if avatars will evolve from flat virtual image concepts to physical digital humans with high intelligence and simulated interactive capabilities, and even assist humans in completing tasks in certain scenarios?
Embodied intelligence refers to integrating artificial intelligence into physical entities such as robots, endowing them with the ability to perceive, learn, and interact dynamically with the environment. Nowadays, embodied intelligence has come to the forefront and has been written into the government work report for the first time.
Humanoid robots are a representative terminal of embodied intelligence, and their core characteristic is emphasizing the dynamic interaction between the robot's body and the environment of the physical world, including physical actions such as grasping, moving, and manipulating objects, which pure software systems such as AI chatbots/AI avatars cannot achieve.

In 2025, humanoid robots have gained significant attention. At the CES conference, NVIDIA announced that nearly half of the 14 humanoid robot manufacturers it collaborates with are from China, including XPENG (Iron), Unitree (H1), Gallbot (G1), Fourier (GR-2), ROBOTERA (Star1), and Agibot (A2).
The development speed of embodied intelligence is faster than imagined. Nowadays, the time interval for new humanoid robots has shortened to days, entering the warm-up phase before mass production. Compared to appearance, the current priority for humanoid robots is to optimize "brain" capabilities and enhance movement capabilities.
On March 11, Zhihui Jun released a new video after two years, showcasing the new Agibot Lingxi X2, which can walk, dance, and ride a bicycle. Prior to this, Zhihui Jun also released the first universal embodied base model, the Agibot Qiyuan large model (Genie Operator-1), which can learn from human videos and training to achieve rapid generalization from small samples, ultimately being deployed onto the body of Agibot.
On March 19, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang delivered a keynote speech at the GTC 2025 conference and announced the launch of the Isaac GR00T N1 universal robot model, enabling universal humanoid robots to understand the human world, follow language instructions, and perform various tasks. Its purpose is to accelerate the development and capability enhancement of humanoid robots.
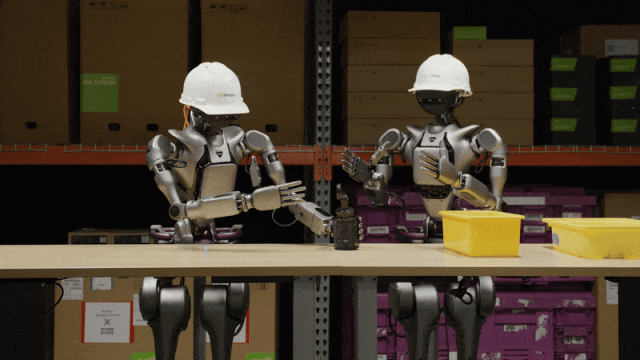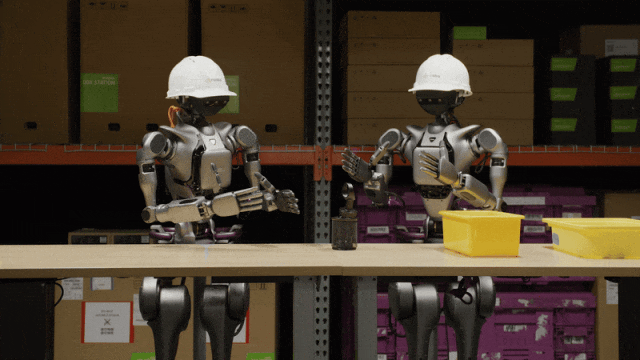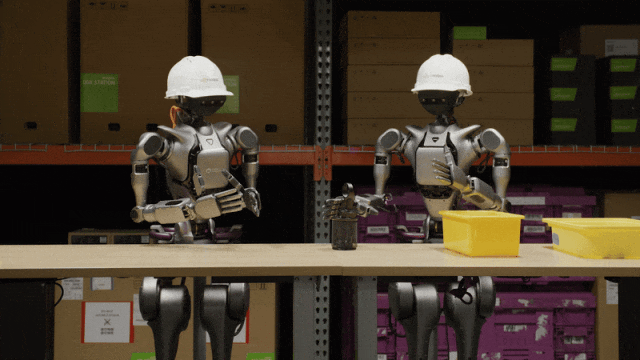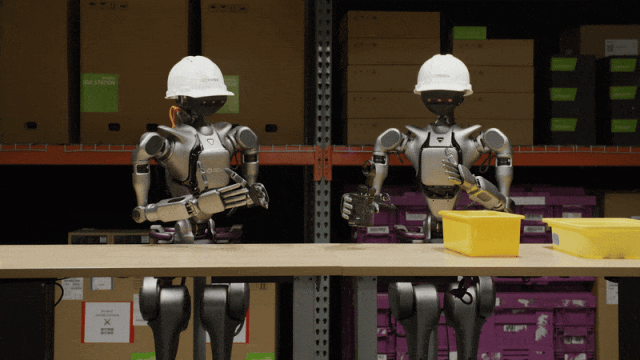
Two Isaac GR00T N1 humanoid robots carrying objects with both arms
Jensen Huang described robots as the next $10 trillion industry and said that by the end of 2030, the world will face a shortage of at least 50 million workers, and more robots will be hired to work in the future.
Unitree's G1 robot's "side aerial somersault" and Boston Dynamics' robot Atlas's "breaking street dance" challenging high-difficulty moves have once again made humanoid robots a hit. These moves require a high level of precision in controlling the movement trajectories and postures of various parts of the robot's body.

Unitree G1 Robot
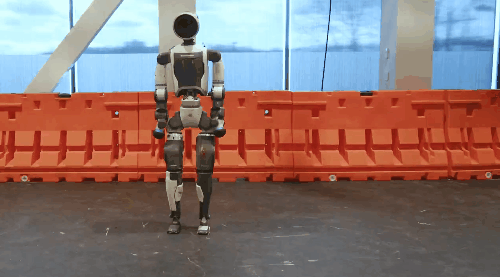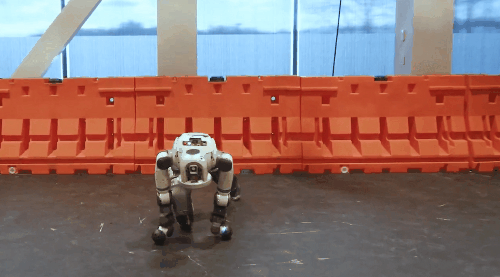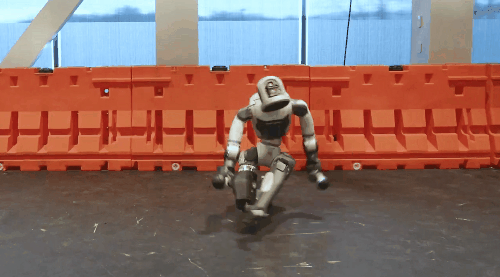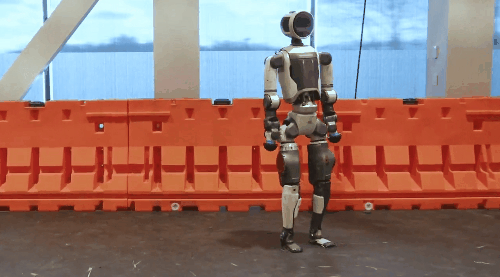
Boston Dynamics' Robot Atlas
The integration of technologies such as computer vision, various sensors, and deep learning is currently propelling humanoid robots towards the application stage. Recommended reading: "China is using a trillion-yuan robot market to alleviate the pension anxiety of two billion people"
Looking back from the technological node of 2025, digital avatars in the virtual world, initially used as entertainment carriers for virtual anchors, now exhibit a new appearance in the real world with embodied intelligence. Although they are vastly different in form, they share some commonalities in technology.
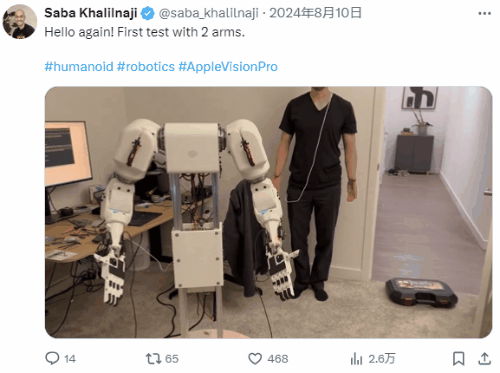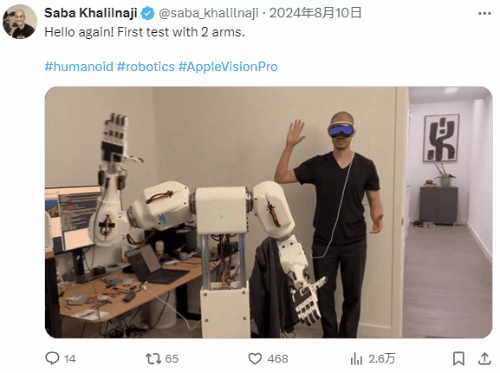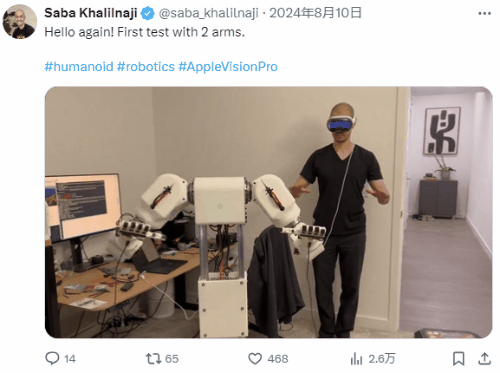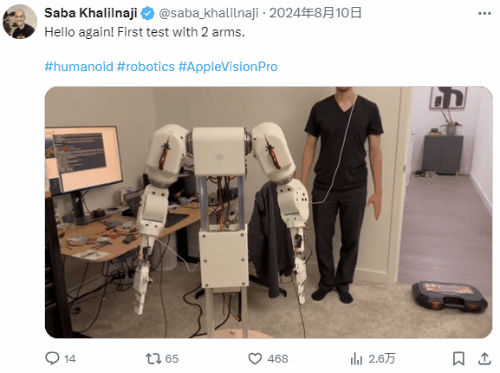
A developer training a robot using Apple Vision Pro
In the long-term development process, digital avatars have evolved into a mature form with complex technical composition and diversified applications, accumulating massive and high-precision motion capture data that has been continuously optimized through training. These valuable data resources can provide solid data support for the training of humanoid robots, helping them to more accurately simulate human movements. Meanwhile, large AI models, with their powerful algorithms and intelligent computing capabilities, endow humanoid robots with core interactive abilities, enabling them to interact more naturally and smoothly with the environment and humans.
We are standing at the boundary where the virtual and the real converge, and may witness the most profound transformation in the production relations in human civilization's history - not robots replacing humans, but human-machine collaboration creating a warmer future.







