Global Auto Industry Amid Tariff Pressure: Dual Challenges for Vehicle Markets and Supply Chains
![]() 04/24 2025
04/24 2025
![]() 435
435

01
Vehicle Market: Diversifying Patterns and Intensifying Regional Rivalries
U.S. Market: Relying on Imports and Regional Rivalries
In 2024, new light vehicle sales in the U.S. hit 16.035 million units, with imports comprising 50% (around 8.01 million units) and import value reaching $243.3 billion. Mexico (2.962 million units), South Korea (1.536 million units), Japan (1.377 million units), and Canada (1.065 million units) emerged as the top four import sources, collectively accounting for 77%, forming the backbone of U.S. vehicle imports. China exported merely 107,000 units to the U.S. (ranking sixth), marginally affected by the current tariff policy.
Impact Analysis of Key Countries
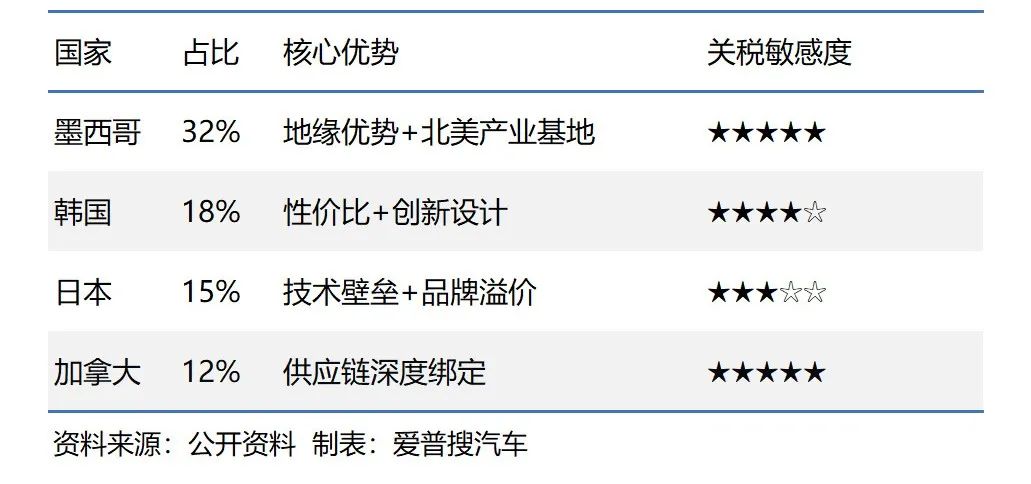
Mexico (32%): Leveraging its geographical advantages and the integrated North American industrial chain, Mexico serves as the "backyard factory" for American automakers like Ford and GM. A 25% tariff hike would lead to a 30%-40% surge in the cost of Mexican-made vehicles entering the U.S., reducing American automakers' profits by over 15% and posing risks of industrial chain relocation.
South Korea (18%): Hyundai and Kia dominate the mid-range market with a "high-configuration, low-price" strategy, but tariffs could cut their per-vehicle profits by over $2,000, potentially raising end prices by 5%-8% and resulting in a 20% sales decline (350,000 units annually). South Korea's dependence on U.S. auto exports stands at 42%, making economic ripple effects inevitable.
Japan (15%): Toyota and Honda rely on technological barriers and brand premiums (e.g., Lexus gross margin exceeding 18%), but tariffs would erode their price competitiveness by 3%-5%, forcing high-end models to pass on costs (e.g., Highlander price increase of $3,000). Major automotive hubs in Kyushu and Aichi face the risk of losing over 50,000 jobs.
Canada (12%): The U.S. and Canada share a "48-hour supply chain circle," with 75% of parts flowing bidirectionally. If Canadian factories shut down for a day, Detroit automaker assembly lines would halt for three days. Tariff increases could push Ontario's auto industry unemployment rate above 8%, threatening the stability of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA).
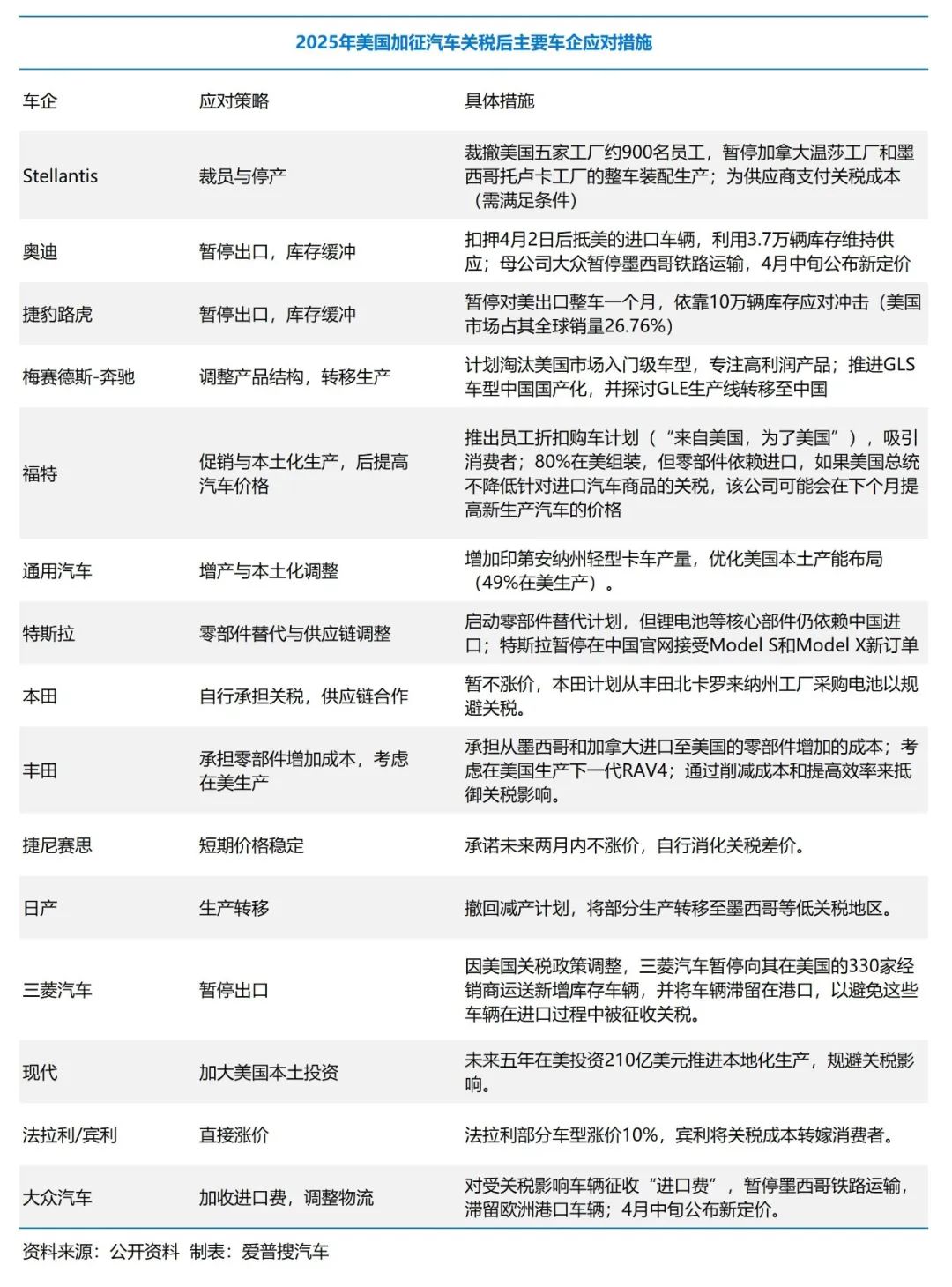
Automaker Response Strategies: Navigating Short-term Survival and Long-term Transformation
Faced with tariff pressure, global automakers adopt differentiated strategies:
02
Supply Chain: Global Fragmentation and Regional Reconfiguration
U.S. Parts Import Dependence and Risk Distribution
In 2024, the total import value of U.S. auto parts amounted to $186.62 billion, with Mexico ($81.17 billion), Canada ($19.47 billion), and China ($18.26 billion) ranking top, collectively accounting for over 60%.
Role of China's Supply Chain: Despite ranking third in parts imports, China remains indispensable in key areas such as lithium batteries and electronic components. Companies like Tesla, reliant on core components imported from China, are compelled to initiate substitution plans but find it challenging to fully achieve "de-China" in the short term.
Globalization Strategy of Chinese Enterprises
Fifteen Chinese companies feature in the global top 100 auto parts list, with CATL (batteries), Fuyao Glass (glass), Joyson Electronics (electronic systems), among others, achieving deep internationalization.
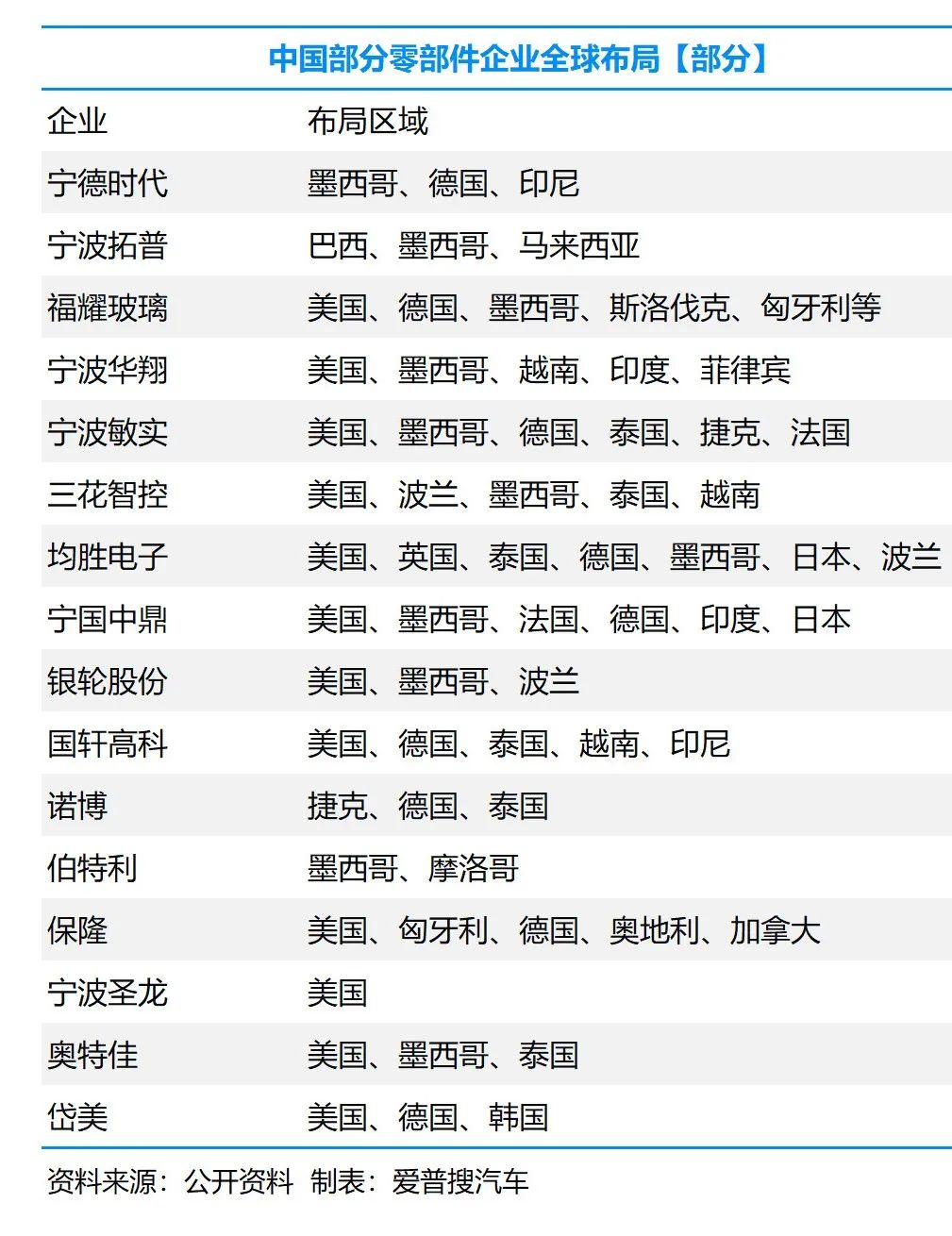
China's Supply Chain: Balancing Offensive and Defensive Maneuvers
Offensive: Overseas factories enable Chinese enterprises to deeply embed themselves in the global industrial chain. CATL, Baolong Technology, and others have achieved "R&D in China, manufacturing worldwide".
Defensive: Enterprises yet to venture overseas need to accelerate transformation to avoid losing international competitiveness due to tariff costs.
Future Trends: The overseas revenue share of Chinese auto parts enterprises is projected to rise from 22% in 2024 to over 40% by 2030, with globalization capabilities becoming a pivotal industry benchmark.
03
Conclusion: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities in the Global Auto Industry
Tariff policies exacerbate regional fragmentation in the global auto industry, compelling automakers and supply chains to accelerate transformation:
Vehicle Market: "Near-shore production" under geopolitical dominance emerges as the norm. Mexico and Southeast Asia benefit from capacity transfers, but technological barriers and cost pressures persist in the long run.
Supply Chain: The globalization capabilities of Chinese enterprises are under scrutiny, and technological autonomy and the depth of overseas layout will shape future competitiveness.
Industry Trends: Amid the electrification and intelligence wave, tariffs are but a short-term disruption, with long-term competition hinging on technological innovation and market response speed.
Future Outlook: If tariff conflicts endure, the global auto industry may evolve into a multipolar structure of "China-U.S.-Europe + regional partners," where supply chain flexibility and resilience become paramount for corporate survival.








