National manufacturing competition, why is Shandong lagging behind
![]() 11/28 2024
11/28 2024
![]() 487
487
National advanced manufacturing cluster competition, Shandong adds 3 more seats.
On November 18, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced the winners of the 2024 advanced manufacturing cluster competition, with a total of 35 clusters nationwide making the list. Qingdao-led Qingdao-Yantai-Weihai Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering Equipment Cluster, Weifang-led Weifang-Linyi-Rizhao Intelligent Agricultural Machinery Equipment Cluster, and Qingdao Instrumentation Cluster were selected, increasing Shandong's total number of selected clusters to 6.
Advanced manufacturing clusters are hailed as the "national team" of manufacturing and are considered "promising stocks" for becoming world-class manufacturing clusters. Since 2019, the MIIT has implemented a special action plan for the development of advanced manufacturing clusters, selecting national-level clusters through a "horse race" approach to support the construction of a modern industrial system with advanced manufacturing as the backbone.
To date, there are a total of 80 national advanced manufacturing clusters in China.

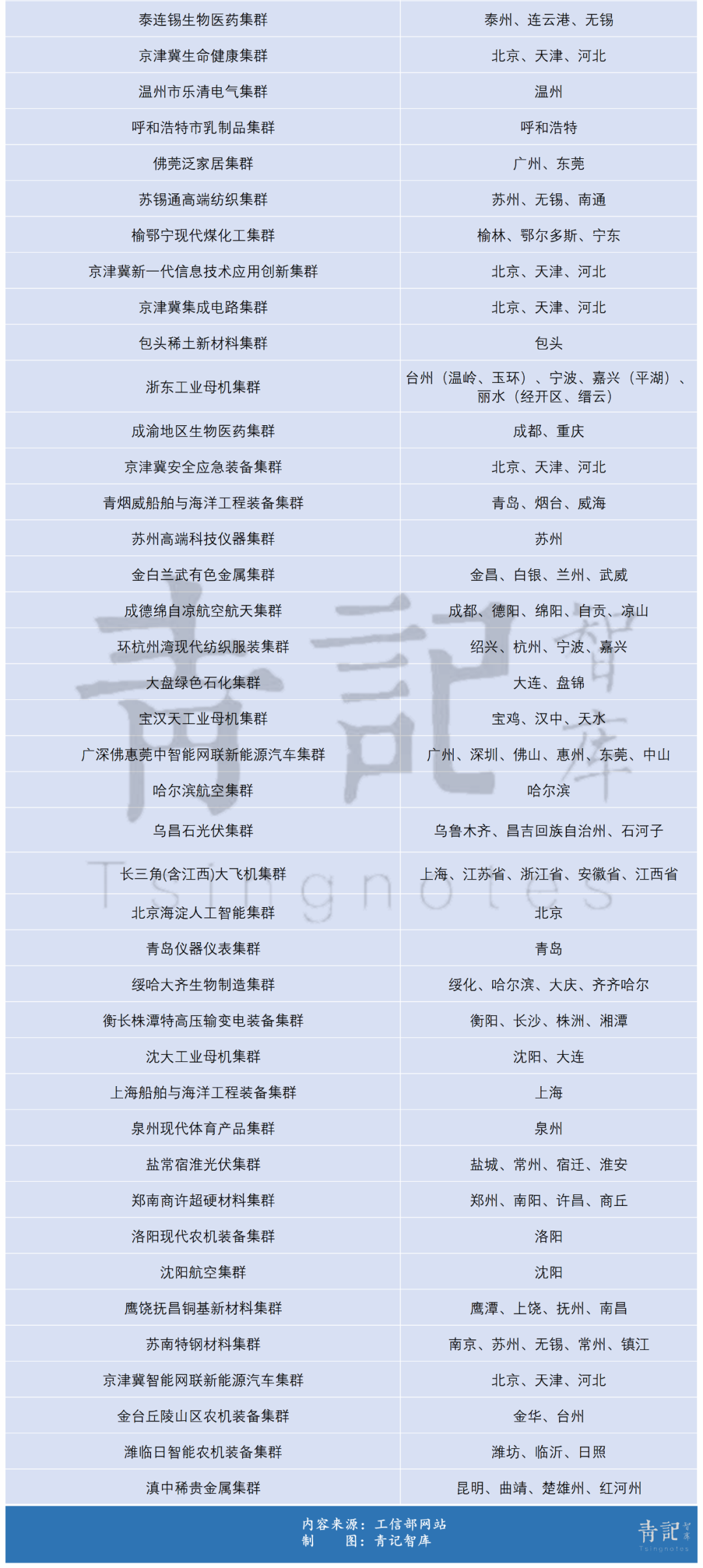
From a city perspective, Beijing, Baoding, and Suzhou each have 6 advanced manufacturing clusters, the highest number. Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Chengdu, Wuxi, Ningbo, and other cities have 5 each, while Qingdao, Nanjing, Dongguan, and others have 4 each.
Among them, many clusters in cities like Beijing, Baoding, Suzhou, Wuxi, Tianjin, and Ningbo are cross-regional collaborative clusters.
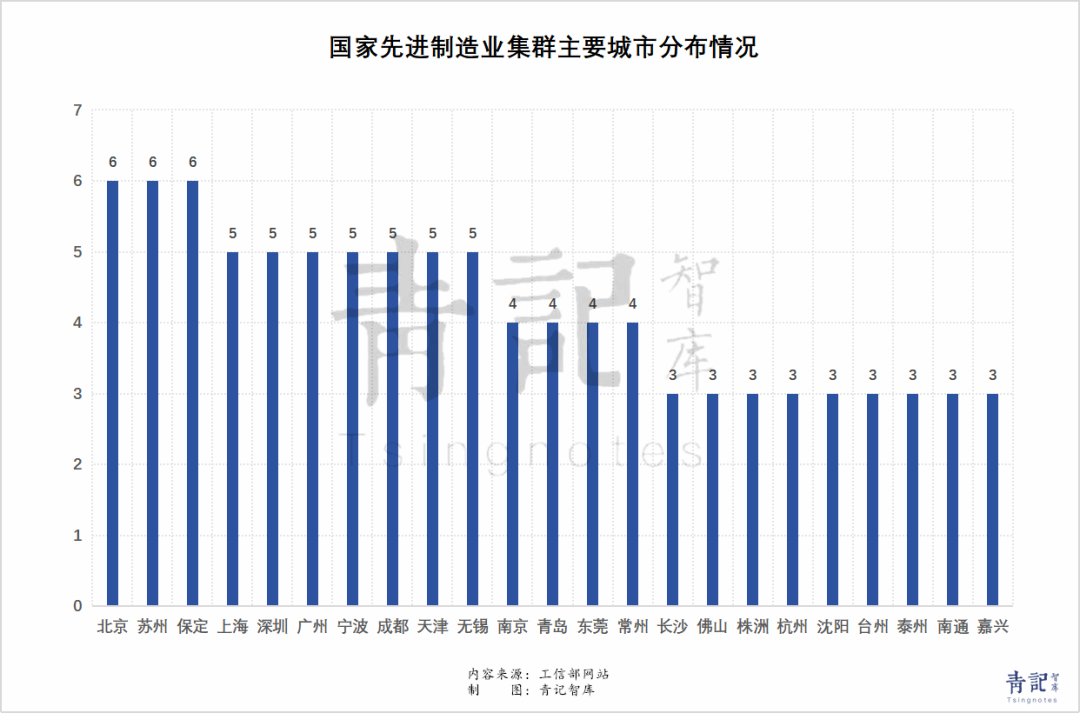
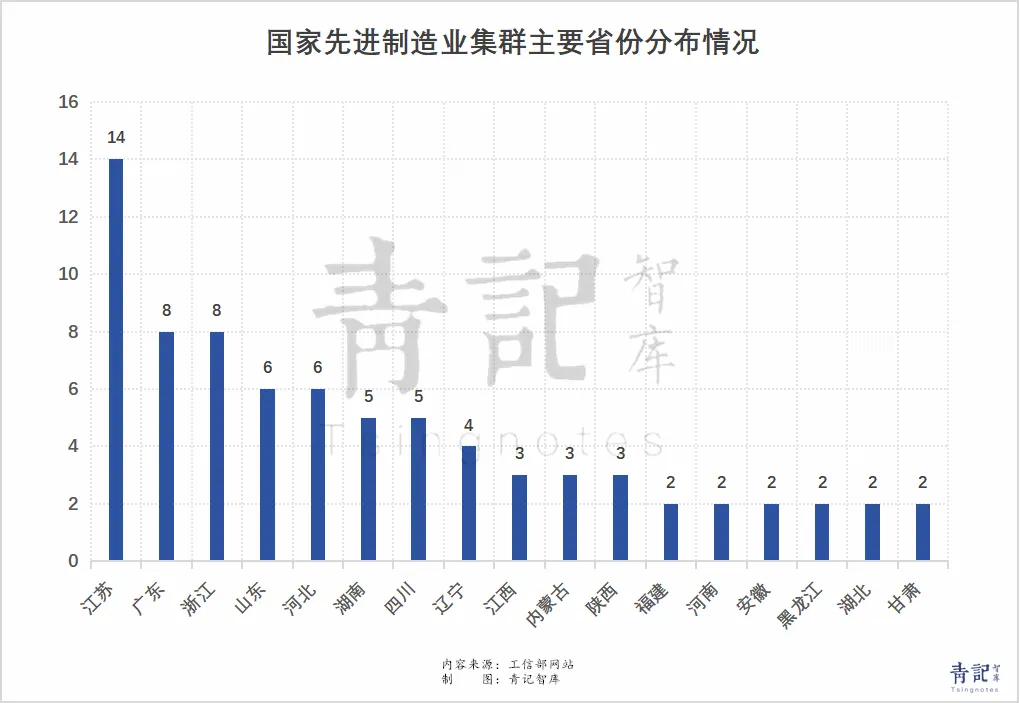
From a provincial perspective, Shandong ranks fourth with 6 selected clusters, trailing only Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Zhejiang, and tied with Hebei.
Notably, in the new round of the national advanced manufacturing competition, more fundamental and high-end manufacturing fields such as machine tools and instrumentation have replaced the new generation of information technology as the focus of national attention.
Against this backdrop, it is worth reflecting that Shandong's long-prided industrial machine tool cluster was not selected.
Shandong needs to pay attention to the cultivation of advanced manufacturing clusters focusing on key basic links and cross-regional collaboration at the provincial level.
1
Overall, the 80 advanced manufacturing clusters cover key areas such as the new generation of information technology, high-end equipment, new materials, biomedicine, new energy, and intelligent connected vehicles, widely distributed across various provinces and cities nationwide.
Comparing the two lists published in 2022 and 2024, there are notable changes.
Among them, the number of clusters focusing on high-end manufacturing is increasing, with clusters such as machine tools and instrumentation achieving zero breakthroughs.
Among the 45 advanced manufacturing clusters announced in 2022, the new generation of information technology was the dominant force.
The selected clusters included the Shenzhen New Generation Information and Communication Cluster, Wuxi IoT Cluster, Shanghai IC Cluster, Nanjing Software and Information Services Cluster, Wuhan Optoelectronics and Information Cluster, and Changsha New Generation Autonomous Secure Computing System Cluster.
The 35 advanced manufacturing clusters announced in 2024 place more emphasis on high-end equipment, such as aerospace equipment, shipbuilding and marine engineering equipment, machine tools, and instrumentation.
Aerospace and shipbuilding are two industries that have developed rapidly in China in recent years. With the construction and commissioning of domestically produced large aircraft and cruise ships, related industries have developed rapidly, giving rise to advanced manufacturing clusters such as the Yangtze River Delta (including Jiangxi) Large Aircraft Cluster, Chengdu-Deyang-Mianyang Aerospace Cluster, Harbin Aviation Cluster, and Shenyang Aviation Cluster.
Machine tools and instrumentation are key equipment in manufacturing.
In the field of machine tools, the Eastern Zhejiang Machine Tool Cluster, Baoji-Hanzhong Machine Tool Cluster, and Shenyang-Dalian Machine Tool Cluster were selected.
Currently, the country's support for the development of machine tools is continuously increasing. For example, the Ministry of Finance and the State Taxation Administration jointly issued a notice to reduce taxes for related machine tool enterprises from 2023 to 2027. The MIIT has deployed the "Machine Tool +" industry-enterprise matching activity, which will continue until the end of 2027, helping enterprises find orders and expand markets.
Zhejiang is a major producer of machine tools, with a 2023 output value of RMB 102.36 billion, making it one of the most concentrated regions for the machine tool industry in China.

It is reported that to promote industry development, Zhejiang has issued the "Zhejiang Province Machine Tool Supply List," introducing a total of 177 equipment items, including metal cutting machines, metal forming machines, metal cutting and welding equipment, and other metal processing equipment, to meet the application needs of different industries.
At the same time, as the main base of the Eastern Zhejiang Machine Tool Cluster, Taizhou has recently signed a series of projects, including the Yuhuan High-end Machine Tool Project, the Annual Production of 20,000 Sets of Ultrasonic Core Components and 500 Sets of Fully Automatic Ultrasonic Cleaning Lines Project, the High-precision CNC Machine Tool and Intelligent Manufacturing Production Line Project, the Linear Motor CNC Machine Tool Project, and the Industrial Robot Intelligent Manufacturing Gripper Project.
2
Another significant change is in cross-regional collaboration.
Among the newly announced 35 advanced manufacturing clusters, 26 are cross-regional collaborative clusters, accounting for over 70%.
To date, there are a total of 37 cross-regional collaborative clusters nationwide, accounting for nearly half.
Specifically, most of the selected clusters in the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta are cross-regional collaborative clusters.
Especially in Guangdong, currently, 6 out of the 8 advanced manufacturing clusters are cross-regional collaborative clusters, such as the Guangzhou-Foshan-Huizhou Ultra HD Video and Smart Home Appliance Cluster, the Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Foshan-Dongguan Smart Equipment Cluster, and the Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Foshan-Huizhou-Dongguan Intelligent Connected New Energy Vehicle Cluster.
The number of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei cross-regional collaborative clusters is also increasing significantly, with 4 new clusters, including the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei New Generation Information Technology Application Innovation Cluster and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei IC Cluster.
In addition, there are also many new cross-regional collaborative clusters in provinces such as Liaoning, Hunan, and Hubei.
Behind this trend is the deepening of industrial integration and collaboration among regions.
For example, the Guangzhou-Foshan-Huizhou Ultra HD Video and Smart Home Appliance Cluster has formed a highly detailed industrial division of labor: air conditioners and refrigerators are manufactured in Guangzhou and Foshan, color TVs and audio-visual equipment are manufactured in Guangzhou and Huizhou, kitchen appliances are concentrated in Foshan, and lighting appliances are concentrated in Foshan, Guangzhou, and Huizhou.
Currently, the leading industry output value of this cluster is close to one trillion yuan. As of 2021, the cluster had gathered over 8,000 enterprises, including 712 above-scale enterprises, 483 high-tech enterprises, and 10 single-champion enterprises.
The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei IC Cluster has Beijing focusing on design and innovation platforms, process and manufacturing innovation platforms, and manufacturing, equipment, advanced packaging manufacturing, and specialized IC design; Tianjin focuses on design to improve the industrial chain and create competitive advantages for key products such as domestically produced CPUs; Hebei focuses on the development of key process technology research and design in the fields of communication networks, Beidou navigation, the Internet of Things, network security, etc., as well as the research and industrialization of core equipment and new materials.
Under coordinated development, the output of ICs in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region has increased from 15.391 billion units in 2018 to 24.546 billion units in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate of 12.4%.
3
In contrast, Shandong's previous lack of emphasis on regional integration and severe disorderly competition due to homogenization in industrial cluster cultivation has become a major shortcoming.
Besides Qingdao (4 clusters) and Weifang (3 clusters), other cities in Shandong have very few national advanced manufacturing clusters.
For example, the industrially strong Yantai only has the newly selected Qingdao-Yantai-Weihai Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering Equipment Cluster; other cities such as the provincial capital Jinan, the traditional industrial hub Zibo, and the private economy-developed Dongying still have zero national advanced manufacturing clusters.
On August 23 this year, the "Jinan-Qingdao-Zaozhuang-Weifang Machine Tool Industry Cluster," jointly declared by Jinan, Qingdao, Weifang, and Zaozhuang, was included in the list.
According to the latest data, the leading industry scale of the Jinan-Qingdao-Zaozhuang-Weifang Machine Tool Industry Cluster currently reaches 46 billion yuan, accounting for 80% of Shandong's total and 12.5% of the national total. It boasts a number of industry-leading enterprises such as Jinan No. 2 Machine Tool Group, Haomai Group, Bestar Laser, and Weida Heavy Industry, with products covering the entire chain from upstream core components such as machine tool bodies, transmission systems, numerical control systems, functional components, auxiliary machines, and consumables to midstream machine tool body manufacturing.
However, Shandong's machine tool cluster was not selected in the new round of national advanced manufacturing cluster winners.
4
Objectively speaking, even Shandong's newly selected Qingdao-Yantai-Weihai Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering Equipment Cluster and Qingdao Instrumentation Cluster have a considerable gap compared to the concurrently selected Shanghai Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering Equipment Cluster and Suzhou High-end Technology Instrument Cluster.
For example, the Qingdao Instrumentation Cluster is the world's largest production base for coordinate measuring machines and the largest ion chromatography industry base in China, with leading enterprises such as Siyi Technology and Hexagon Metrology, as well as over 1,000 technology-based enterprises, leading domestically in multiple sub-fields such as industrial measurement and control, electronic measurement, environmental monitoring, and marine observation.
The Suzhou High-end Technology Instrument Cluster, with Suzhou Industrial Park as its core area, gathers over 700 high-end technology instrument-related enterprises within the core area, nurturing 8 listed companies with a total industrial scale of nearly 40 billion yuan. Its leading products, such as BMS chip testing equipment and mechanical testing equipment, have the highest market share in China.
For Shandong, special attention needs to be paid to the value of its manufacturing clusters.
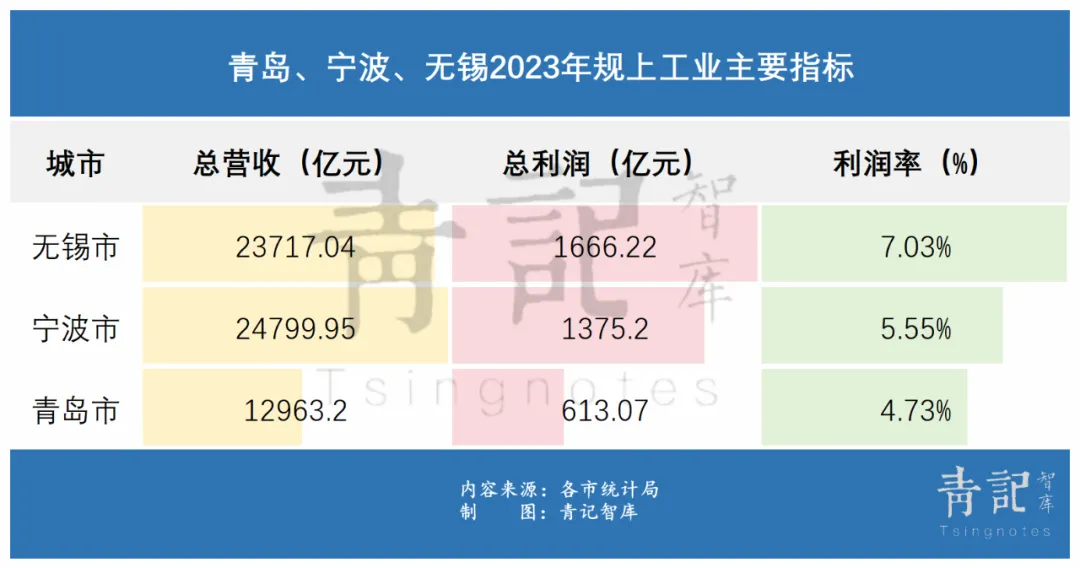
Taking Qingdao, which has the largest number of selected clusters in Shandong, as an example, Qingdao has only one fewer national advanced manufacturing cluster (4, including 1 cross-regional) than Ningbo (5, including 2 cross-regional) and Wuxi (5, including 3 cross-regional), which have similar GDP levels. However, Qingdao's overall industrial revenue and profit are less than half of those of Ningbo and Wuxi.