Smartphone Battle 2025: Predictions and Strategies for the Evolving Market
![]() 01/23 2025
01/23 2025
![]() 410
410

[Original by Tidal Business Review]
A dealer in Ningbo, Zhejiang, reflects on the current state of the mobile phone market: "Last year was challenging for all manufacturers, with constant price adjustments and inventory pressures. Huawei, which once did not share inventory, became a key supplier. However, this year started on a positive note. With national subsidies kicking in on the 20th, store foot traffic and sales surged, and representatives from various brands have been in touch daily to discuss policies and quantities."
The smartphone industry stands on the brink of a major reshuffle and transformation in 2025!
The "national subsidies" mentioned pertain to a mobile phone replacement subsidy policy gradually rolled out nationwide since January 20th. Additionally, on January 17th, a significant event shook the industry: Zhao Ming, the driving force behind Honor, announced his resignation as CEO due to health reasons, sparking widespread discussions.
These successive events at the start of 2025 have rendered the competition among mobile phone manufacturers unpredictable. One thing is certain: with Huawei's return, the existing brand landscape will be disrupted, potentially reverting the market to the pre-pandemic "Huawei era." Other brands, besides staying rooted in their domestic bases, might need to intensify their overseas efforts.
01 Transformation: Mobile Phone Market Rebounds, Brand Dynamics Fluctuate
The recovery of the smartphone industry is highly probable. In 2024, the market witnessed its first growth after two consecutive years of decline. CIDC data shows that annual smartphone shipments in mainland China reached 286 million units, up 5.6% year-on-year. With improved consumption conditions and AI technology advancements, growth is likely to continue.
This growth stems from continuous innovation in mobile phone products across China and the introduction of consumption stimulus policies in various regions, gradually unleashing pent-up demand for phone replacements.
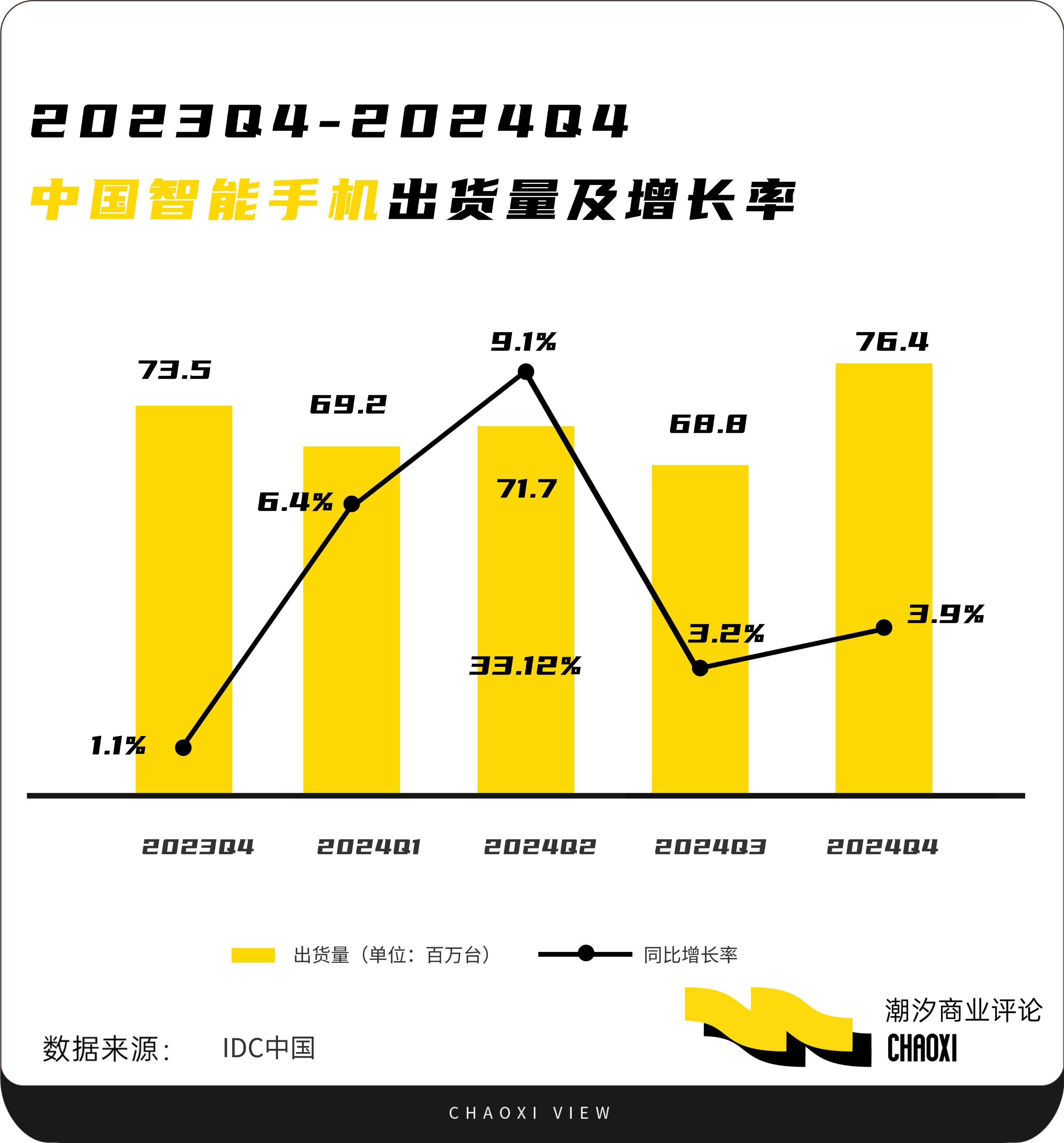
A senior analyst at Canalys noted in a report, "Manufacturers' technological innovations have clearly spurred high-end prosperity and mass demand recovery in the Chinese market. For instance, Huawei's HarmonyOS, Xiaomi's PentaOS, Honor's large-mAh Qinghai Lake battery, and foldable screen innovations continue to captivate high-end users and drive upgrades."
Since the beginning of this year, high-end mobile phones have experienced notable structural growth. Data from authoritative institutions shows that in the first three quarters of 2023, Huawei's share of high-end sales surged by 34%, while Xiaomi achieved an 88% increase with the Xiaomi 15 series. OPPO's Find X8 series, for example, saw a 66% year-on-year shipment increase in the first sales quarter compared to the previous generation, making it the flagship model with the largest growth among various manufacturers.
In the mass market, brands like Honor, OPPO, and vivo continue to offer high-end design, robust, and affordable products in the 1K-3K and above 4K price ranges, encouraging phone replacements.
Public data reveals that in 2024, Redmi released 10 new models, OPPO 19, vivo 28, and Honor also 28. These launches drove market development and increased consumer demand for new phones.
Coinciding with the concentrated model releases, purchase subsidies followed, further boosting mobile phone sales.
A Jiangsu telecommunications dealer shared, "Buying a phone within our province entitles you to a 15% subsidy. For instance, the original Huawei P series, priced around 5000 yuan, costs consumers just over 4000 yuan. During the subsidy's launch month, store sales nearly tripled, with noticeable increases across brands."
With national subsidies landing on JD.com on January 20th, mobile phone sales surged 200% compared to the previous month in the first 12 hours.
Despite these favorable factors pointing to industry growth, mobile phone manufacturers face a mixed bag. vivo topped the market share with 17%, while Apple's shipments declined by 17%, the steepest drop among all brands. Huawei's resurgence is evident, with shipments up 37% year-on-year in 2024, totaling 46 million units. It's anticipated that in 2025, Huawei will soon surpass vivo to reclaim the domestic top spot.
Thus, in 2025, the domestic mobile phone market's leading manufacturer landscape will shift from five to six, intensifying domestic competition over the next 2-3 years.
02 Competition: Huawei as the Game-Changer, Intensifying the Mobile Phone Battle
The key variable in this scenario stems from Huawei's return, bringing both certainty and uncertainty.
Certainty lies in Huawei's potential to reclaim its 2020 peak, further compressing other brands' market space. By Q2 2019, Huawei had surpassed Apple to become the world's second-largest mobile phone manufacturer. In 2020, with a 44.1% market share, it overtook Apple to lead the high-end market.
Despite past chip supply challenges, after years of recovery and development, the latest supply chain news indicates Huawei aims to capture the top domestic market share and enter the global top five by 2025.
Uncertainty surrounds how long other brands can survive under Huawei's pressure. Current brand situations reveal:
Apple is losing ground in the high-end market;
OV's share is affected offline;
Honor faces significant pressure;
Xiaomi lacks scale for now.
Wang Ming (pseudonym), an authorized dealer of iPhone and OV in Hangzhou for over a decade, considered switching to domestic brands last December. He bluntly shared his insights on several brands.

"Huawei Mate 70's premium was evident, and the original nova and P series sold well. More consumers chose them, boosting Huawei's sales share from 10% to about 45% of our entire system, while other brands' sales plummeted. Some didn't even open daily. Even Apple's high-end models declined by over 30% here."
Even Honor, spun off from Huawei, faces considerable pressure. A mobile phone dealer noted, "The 15% national subsidy may accelerate industry sales differentiation. For instance, compared to last year's first half, our Honor purchases reduced, especially towards year-end. Many stores now prioritize Huawei promotions."
OV's offline channel system grapples with internal friction and costs.
An OV store owner said, "Over 90% of stores compete on price. Though the profit margin is said to be 18%-25%, retail price purchases are impossible now. Sometimes, a machine worth two or three thousand yuan earns just over a hundred yuan."
Rumors suggest vivo offered a 40%-50% rent subsidy to eligible authorized stores last May. However, facing the demand for new vivo stores, different channel providers remain cautious.

In the county market, a well-located and decorated vivo authorized experience store incurs annual rental costs of 80,000-100,000 yuan, renovation costs of 50,000-70,000 yuan, and stocking costs as high as 200,000-300,000 yuan, not including daily operating expenses.
Even with a 40%-50% rent subsidy for eligible stores, given the comprehensive gross profit margin of less than 10% and annual mobile phone shipments of just 100-200 units, the payback period becomes crucial. Notably, in the township market, high-end flagship models like vivo's X series and XFOLD series, priced above 3000 yuan, are virtually unsellable compared to Huawei's P series and others.
Xiaomi fairs better. Unlike other distribution-tied brands, Xiaomi relies on exclusive stores for offline survival. However, its market size is smaller, failing to rank in last year's domestic top five.
The intense mobile phone battle may become a major industry theme in 2025. Finding new growth avenues will be most brands' strategic focus, with increased overseas efforts being an inevitable option.
03 Evolution: Expanding Overseas, Shifting to New Frontiers
Accelerating overseas expansion is crucial as Huawei's advancement pressures other brands into two strategies: holding onto the domestic base and expanding overseas to survive.
Regarding the domestic base, it's uncertain if Huawei's return will maintain past momentum, as other brands have built comprehensive competitiveness. For example, Honor created AI-driven competitive products, with Magic7 introducing features like YOYO Assistant and AI Magic Photography.

With life-or-death yet to be decided and Apple experiencing the steepest decline last year, domestic brands are likely to comprehensively challenge Apple in 2025. Other domestic brands, though impacted by Huawei, should retain their domestic base, especially offline, with tens of thousands of counters and stores.
However, facing a formidable opponent like Huawei, vigilance is crucial. Thus, intensifying overseas market layouts has become a consensus among domestic brands, evident from their overseas performances.
In December, Honor announced that overseas sales reached 50%, on par with China, vowing to expand in European and American markets. OPPO's overseas shipments account for about 60%, continuing to expand overseas offline zones. vivo focuses on localized operation strategies in various markets, while Xiaomi entered South Korea on January 15, 2025.
This is because, on one hand, the global smartphone market still has growth potential. IDC data shows that global smartphone shipments increased by 6.4% year-on-year in 2024, totaling 1.24 billion units, projected to reach 1.27 billion units in 2025, with a year-on-year growth rate of at least 3%. This lucrative pie offers new imaginings for domestic brands eyeing overseas expansion.
On the other hand, considering Huawei's phones have faded from overseas markets for years, and the complex environment makes hasty efforts unlikely, its focus remains on the domestic market. This means Huawei has temporarily ceded the global market, increasing opportunities for other brands.
While Apple and Samsung maintained the top two global shipment volumes in 2024, they saw market share declines of 0.9% and 1.4% year-on-year, respectively, under Chinese brands' strong offensive. Xiaomi's annual shipments reached 168 million units, up 15.4% year-on-year, the most significant growth.
However, the overseas market is Apple and Samsung's core base. Domestic brands focus on a strategy of taking major countries one by one to tell stories in new battlefields. For instance, in Europe, Honor targets the high-end market with the Magic series and digital series, while in Indonesia and Southeast Asia, it aims at the mid-to-high-end segment above 300 USD. This differentiated approach caters to various regional and demographic needs, enabling Honor to swiftly enter markets and gain consumer favor. OPPO and vivo adhere to localized methodologies by establishing overseas production bases for supply chain diversification and localization.
The overseas mobile phone market is substantial. Similar to the collective overseas expansion of Chinese new energy vehicles, other domestic mobile phone brands are upgrading their overseas expansion strategies amidst competition from Huawei and others. They are accelerating the transition from the initial overseas 1.0 era to a more extensive 2.0 era, ensuring that overall sales remain stable.
04 Conclusion
Since the advent of the iPhone 4, mobile phones have been evolving towards the era of smart terminals for over a decade. Competition within China's mobile phone industry shows no signs of abating, transitioning from price wars to technical parameter battles, and now to brand strength contests. From Apple's early dominance to domestic supremacy today, the current six mainstream brands have formed a landscape of "one superpower and many strong contenders."
Within this landscape, Huawei's offensive will intensify. As Hu Baishan, Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer of vivo, noted, "Huawei's return to the Chinese mobile phone market has emerged as the primary variable, essentially aiming to reclaim its rightful market share."
In 2025, it remains uncertain which domestic mobile phone brand will lag behind and which will achieve new growth through overseas expansion and other strategies.







